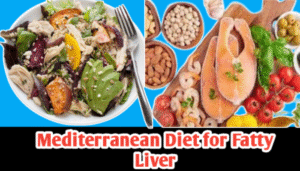
Mediterranean Diet for Fatty Liver disease occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver cells, impairing liver function. It can be non-alcoholic (NAFLD) or alcohol-related. NAFLD is increasingly common due to sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, and obesity.
A well-planned Mediterranean diet has been scientifically proven to reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and support overall metabolic health. This guide provides practical strategies, food recommendations, and lifestyle tips to manage and reverse fatty liver.
1. What is the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet is based on the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain.
Key characteristics include:
- High intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Moderate consumption of fish and poultry.
- Olive oil as the primary fat source.
- Minimal intake of red meat, processed foods, and added sugars.
This diet is rich in antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats, making it particularly beneficial for liver health.
2. Why the Mediterranean Diet is Beneficial for Fatty Liver
The Mediterranean diet supports liver health through multiple mechanisms:
2.1 Reduces Liver Fat
- High-fiber foods like vegetables, legumes, and whole grains help mobilize fat from the liver.
- Monounsaturated fats (olive oil) prevent fat accumulation in liver cells.
2.2 Supports Weight Management
- Balanced meals with high fiber and healthy fats increase satiety, reducing overeating.
- Weight loss of even 5–10% can significantly improve liver function.
2.3 Improves Insulin Sensitivity
- Whole grains and legumes stabilize blood sugar, reducing insulin resistance, a key factor in NAFLD.
2.4 Reduces Inflammation
- Antioxidant-rich foods (berries, leafy greens, tomatoes) and omega-3 fatty acids reduce oxidative stress, lowering liver inflammation.
2.5 Supports Heart Health
- Fatty liver is often linked to cardiovascular risk. The Mediterranean diet lowers cholesterol and triglycerides, protecting both liver and heart.
3. Core Principles of a Liver-Friendly Mediterranean Diet
To maximize liver benefits, the diet should follow these principles:
3.1 Emphasis on Fruits and Vegetables
- Aim for 5–10 servings daily.
- Include leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, and colorful fruits for antioxidants and fiber.
3.2 Whole Grains
- Choose brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, and whole-grain bread/pasta.
- Provides fiber to regulate blood sugar and reduce liver fat.
3.3 Lean Proteins
- Focus on fish (salmon, sardines, tuna), legumes, lentils, and moderate poultry.
- Avoid excessive red meat, which can increase liver fat.
3.4 Healthy Fats
- Primary fat: extra virgin olive oil.
- Include nuts, seeds, and avocado for monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
3.5 Limit Added Sugars and Processed Foods
- Avoid sugary drinks, desserts, refined grains, and fried foods.
- Excess sugar promotes fat accumulation in the liver.
4. Mediterranean Diet Foods to Include for Fatty Liver
A liver-friendly Mediterranean diet emphasizes nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods:
4.1 Vegetables & Fruits
- Examples: Spinach, broccoli, kale, zucchini, carrots, tomatoes, berries, oranges.
- Benefits: Fiber promotes fat metabolism; antioxidants reduce inflammation.
4.2 Whole Grains
- Examples: Brown rice, oats, quinoa, barley, whole-grain pasta/bread.
- Benefits: Steady energy, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced liver fat.
4.3 Legumes & Lean Proteins
- Examples: Chickpeas, lentils, beans, tofu, fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel).
- Benefits: Protein supports muscle health and satiety without adding harmful fats.
4.4 Healthy Fats
- Examples: Olive oil, avocado, nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds (chia, flax).
- Benefits: Reduces inflammation, improves lipid profile, and prevents liver fat accumulation.
4.5 Herbs and Spices
- Examples: Garlic, basil, oregano, rosemary, turmeric.
- Benefits: Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties enhance liver protection.
5. Foods to Avoid or Limit for Fatty Liver
Certain foods exacerbate liver fat and inflammation:
5.1 Sugary Beverages
- Soda, sweetened juices, and energy drinks increase liver fat and insulin resistance.
5.2 Refined Carbs
- White bread, pastries, and white rice spike blood sugar, promoting fat accumulation in the liver.
5.3 Fried and Processed Foods
- Fast food, packaged snacks, and fried items contain trans fats that harm liver health.
5.4 Red Meat and High-Fat Dairy
- Limit beef, pork, and full-fat cheese; these are high in saturated fats that worsen NAFLD.
6. Sample Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan for Fatty Liver
A daily liver-friendly meal plan can guide practical implementation:
6.1 Breakfast
- Oatmeal topped with blueberries, chia seeds, and a drizzle of olive oil.
- Green tea or black coffee (unsweetened).
6.2 Mid-Morning Snack
- Handful of walnuts and an apple.
6.3 Lunch
- Quinoa salad with chickpeas, cucumber, tomatoes, olives, and olive oil-lemon dressing.
- Steamed broccoli or roasted vegetables on the side.
6.4 Afternoon Snack
- Carrot and celery sticks with hummus.
6.5 Dinner
- Grilled salmon with roasted zucchini, bell peppers, and brown rice.
- Side salad with olive oil and balsamic vinegar.
6.6 Optional Dessert
- Fresh berries or a small portion of fruit salad.
7. Lifestyle Tips to Support Fatty Liver Recovery
Along with diet, lifestyle changes are crucial for reversing fatty liver:
7.1 Regular Physical Activity
- Aim for 30–45 minutes of moderate exercise daily.
- Includes walking, swimming, cycling, or resistance training.
7.2 Weight Management
- Even 5–10% weight loss significantly improves liver function.
- Combine diet and exercise for sustainable results.
7.3 Hydration
- Drink plenty of water to aid metabolism and liver detoxification.
7.4 Limiting Alcohol
- Alcohol contributes to liver damage; avoid or minimize intake.
7.5 Stress Management
- Chronic stress affects liver metabolism.
- Include yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overeating even healthy foods.
- Skipping fiber-rich vegetables and whole grains.
- Neglecting exercise and lifestyle factors.
9. Conclusion
The Mediterranean diet is scientifically proven to reduce liver fat, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall liver health. By focusing on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while avoiding added sugars, refined carbs, and processed foods, you can manage and even reverse fatty liver disease.
Combining this diet with regular exercise, proper hydration, and stress management maximizes liver protection and supports long-term wellness.